Climbing the Gradient: A Beginner's Guide to Gradient Descent in Machine Learning
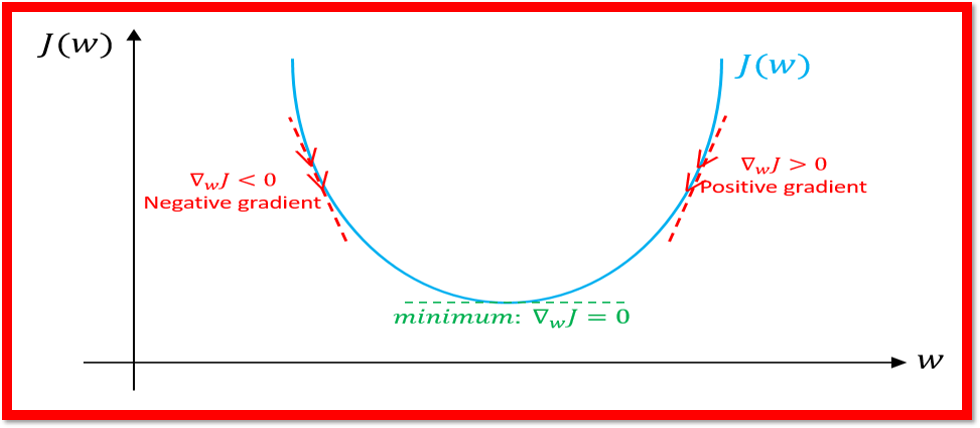
Gradient descent is a widely used optimization algorithm in machine learning that helps adjust the parameters of a model to minimize the cost function. The goal is to find the set of parameters that produces the lowest cost.
Imagine you're trying to find the shortest path down a steep hill. To do so, you would start at the top of the hill and move in the direction of the steepest descent until you reach the bottom. The gradient of the hill, represented by the slope, would guide your movement.
In the context of machine learning, the hill represents the cost function, and the parameters of the model are the coordinates on the hill. By computing the gradient of the cost function with respect to the parameters, you obtain the direction of steepest descent. The model then updates its parameters in the opposite direction of the gradient, moving closer to the minimum of the cost function.
This process is repeated multiple times (iterations) until the cost function reaches a minimum value, indicating that the model has found the optimal set of parameters.
For example, let's say you're training a linear regression model to predict house prices. The parameters of the model are the slope and the intercept. The cost function measures the difference between the predicted prices and the actual prices. Gradient descent adjusts the slope and intercept of the model by moving in the direction of the steepest descent of the cost function, reducing the error and improving the predictions.
Cheers!! Happy reading!! Keep learning!!
Please upvote if you liked this!! Thanks!!
You can connect with me on LinkedIn, YouTube, Kaggle, and GitHub for more related content. Thanks!!